How to find the sine of the angle of a triangle?
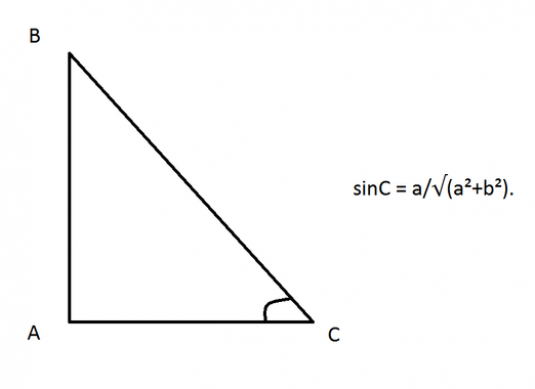
To find the sine of the angle of a rectangular triangle, we need to remember what a sine is by definition. And the definition is very simple: the sine of the angle is equal to the ratio of the opposite leg to the hypotenuse.
How to calculate sines
If we have a triangle ABC, for which A -a right angle, then the sides AB and AC will be the legs, and the side BC - the hypotenuse. Hence, by definition, the sine of angle B is equal to the ratio of the leg of AC to the hypotenuse: sinB = AC / BC, and the sine of the other angle sinC = AB / BC.
In a right-angled triangle, the functions of the anglesit is convenient to calculate: no additional constructions are needed. It is enough to know the length of the right sides. But more often only a part of the necessary data is known, the rest should be sought. Consider how to do this.
Looking for a sine by two legs
We take the same triangle ABC with a right angle A, in which we know the dimensions of the legs: AB = a, AC = c. To calculate the sine of angle C, it is necessary to divide the cathete into a hypotenuse:
- sinC = AB / BC = a / BC (1).
But the hypotenuse will have to be considered according to the Pythagorean theorem:
- BC = √ (AB² + AC²) = √ (a² + b²). (2)
We supply the found value of the hypotenuse (2) in expression (1), we get the answer:
- sinC = a / √ (a² + b²).
Looking for a sine on the hypotenuse and the adjacent leg
Now, in the same triangle, we need to find the sine of the same angle C, but we know the hypotenuse BC = b and the cathode AC = c. With the help of the Pythagorean theorem: AB² + AC² = BC² we look for the AB:
- AB = √ (b²-c²).
Now substitute the found value of AB in the formula for the sine:
- sinC = AB / b = √ (b²-c²) / b.
Sine calculation on one side and sharp corner
In the triangle ABC with a right angle A, the angle B = β is known, and the catethesis AC = c. We need to find the sine of the angle C.
Method 1.
The simplest - if you recall that the sum of all the angles in the triangle is 180 °:
- A + B + C = 180 °.
- The angle A = 90 °, B = β,
- C = 180 ° -90 ° - β = 90 ° - β.
- Hence sinC = sin (90 ° - β).
Method 2.
But you can go the other way:
- Sinβ = AC / BC; Sinβ = c / BC. From here:
- BC = c / Sinβ.
From the theorem of Pythagoras AB2 + AC2 = BC2 we find the hypotenuse:
- AB = √ (BC²-AC²).
We substitute the known values:
- AB = √ (с² / Sin²β-c²) = √с² (1 / Sin²β-1) = с√ (1 / Sin²β-1).
Hence we find the sine of the angle C:
- sinC = AB / BC = c√ (1 / Sin²β-1) / s / Sinβ = Sinβ √ (1 / Sin²β-1)
Answer:
- sinC = Sinβ √ (1 / Sin²β-1).