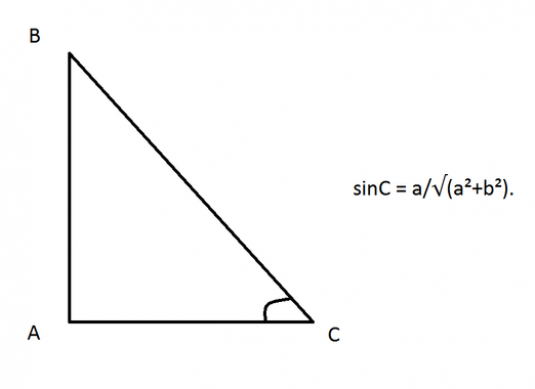How to find a sine if the cosine is known?
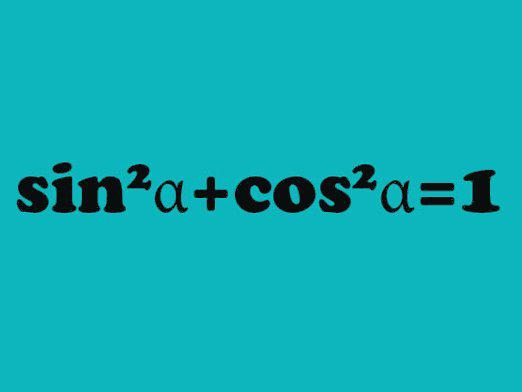
When a problem is given in which one is knowntrigonometric function, and it is required to find another trigonometric function, it is not difficult to solve it. But it is very important to take into account the small subtleties in the solution. Consider the detailed solutions, given the nuances. There are several variants of problems in which it is required to find a sine if the cosine is known.
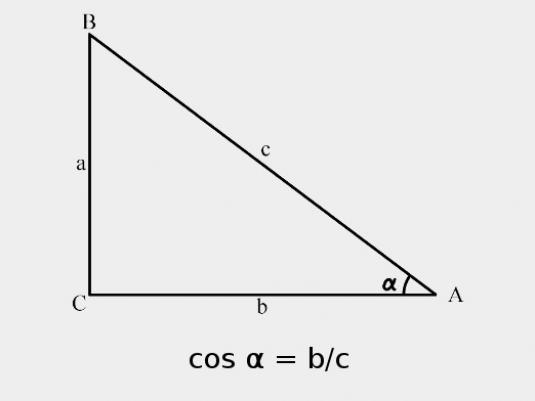
Variant 1. A rectangular triangle is given. The cosine of the angle of this triangle (not the right angle) is known. Nastya is a sine.
Decision:
Recall the basic trigonometric identity: sin2α + cos 2α = 1.
Hence sin2α = 1 - cos2α.
sin α = ± √ (1- cos2α)
In a right-angled triangle, the value of the angle (not direct) can lie in the range from 10 up to 890. The sine of such an angle is always positive, therefore, before the root, we will have a plus.
Variant 2. The cosine of some angle is known. It is also known to which quarter of the trigonometric circle the angle belongs.
Decision:
sin2α + cos 2α = 1.
sin2α = 1 - cos2α.
sin α = ± √ (1- cos2α)
It is known that the trigonometric function is sinecan take values from -1 to +1. Therefore, when extracting the root, we must take this into account. Depending on which quarter belongs to the angle, put a sign in front of the root "+" or "-".
What are the quarters:
- I (first) - α from 00 up to 900;
- II (second) - α from 900 up to 1800;
- III (third) - α from 1800 up to 2700;
- IV (fourth) - α from 2700 up to 3600.
If the angle belongs to the first or second quarters, then we do not put the root "-" before the sign, since in this case sin α is always positive.
If the angle belongs to the third or fourth quarter, then before the root sign we put "-", since in this case sin α is always negative.
Example. Given the cosine, find the sine. cos α = v3 / 2. Angle in the fourth quarter.
Decision:
So, how to find the sine, knowing the cosine:
sin α = ± v (1- cos2α)
Since by the assumption of the problem the angle belongs to the fourth quarter of the trigonometric circle, we put the sign "-" before the root.
sin α = -v (1-3 / 4)
sin α = - 1/2.
Example. In a rectangular triangle, the cosine of one angle is 1/2. Find the sine of this angle.
Solution: sin2α + cos 2α = 1.
sin2α = 1 - cos2α.
Since we are looking for the angle of a right-angled triangle, the "+" sign in front of the root.
sin α = v (1- cos2α)
sin α = v (1-1 / 4)
sin α = v3 / 2.