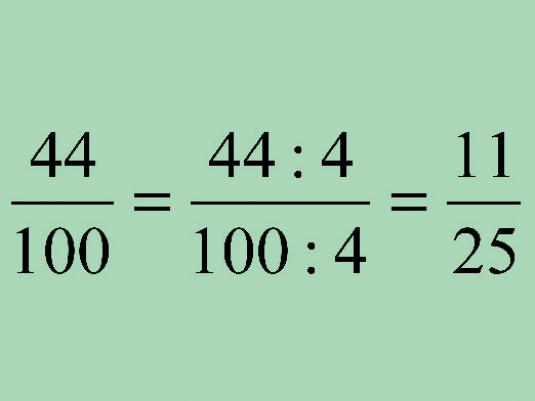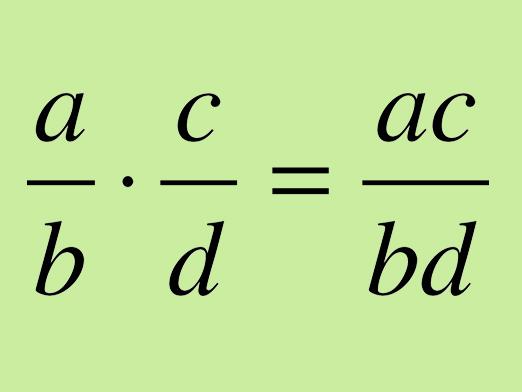What are fractions called?

In mathematics, a fraction is a number consisting ofone or more parts of a unit. That is, the fraction represents some part of one whole. For example, if an object is divided into 4 equal parts and one of them is taken, then we obtain a fraction 1/4, where 3 is a numerator, 4 is a denominator, and the result of this division (0.25) is a quotient. In the school program, different fractions are used, as they are called, depends on their kind.
Ordinary, decimal and periodic fractions
By the method of recording, ordinary anddecimal fractions. In the first case, the fraction is also called simple. It consists of two natural numbers, separated by a horizontal or oblique stroke, as in the image below.
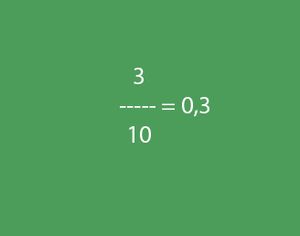
A decimal fraction is an ordinary fraction withdenominator in the form of a unit with subsequent zeros, an example of such a fraction is given in the following figure. However, such fractions are usually written without a denominator, and a comma (0.3) is used to denote the part from the whole. In this case, after the comma, as many digits as there are zeros in the denominator of a simple fraction are indicated.
In the latter case, we are talking about periodicfractions, because the repeated numbers were called the period. In this case, the period is usually enclosed in brackets, for example, 2, (3). This entry is read as follows: two whole and three in the period. However, periodic fractions can be rounded, then they are often called round fractions, although in mathematics it will be more correct to say - a rounded fraction.
Correct, irregular and mixed fractions
A fraction is called correct when the modulus of the numerator is less than the modulus of the denominator

At the same time, any irregular fraction can be represented as a mixed fraction, an example of such a fraction is given below.

Here 1 is this integer part of the mixed number, and1/2 is the fractional part. To convert a mixed number into a fraction, multiply the whole part by the denominator and add the numerator to the obtained value. As a result of such actions, the numerator of the ordinary fraction is found, while the denominator remains the same.
Reducible and irreducible fractions
When the numerator and the denominator of a fraction can be divided into the same number (except one), the fraction is called contractible, in any other case it is irreducible. For example:
- 3/9 is a reducible fraction, since both the numerator and the denominator can be divided by 3;
- 3/5 is an irreducible fraction, since both numbers are simple; divide only by themselves and by 1;
- 2/7 is an irreducible fraction, since there is no total number divided by both the numerator and the denominator.
Composite and inverse fractions
Often, students do not understand what fractionis called the inverse, and which is composite. It turns out that everything is quite simple. If we take the fraction 7/8 and swap the numerator and the denominator, then we obtain a fraction of 8/7. It is these fractions (7/8 and 8/7) that are called inverse fractions. Moreover, it should be noted that the product of such fractions is always 1.
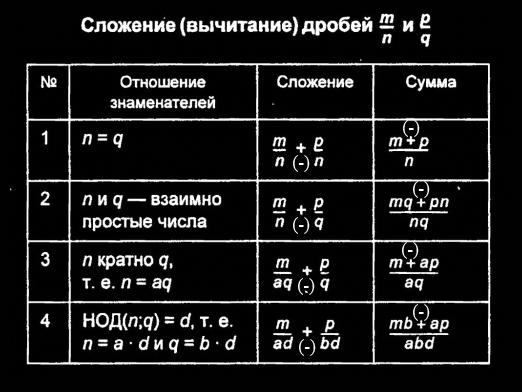
Composite fractions include expressions involving several features of the fraction. Examples of such fractions are given below.

In addition, there are positive and negative fractions. To denote the last before the fraction is put a sign "-". In this case, the sign "+" usually does not indicate, as in the case of positive numbers.