How do the kidneys look?
Kidneys - located in pairs in the lumbarthe area of organs similar in shape to beans. The weight of each of them is about 130-150 g. To understand how the human kidneys look, look at the pork kidneys that are sold in the meat section: the shape and size of these organs in humans and pigs are approximately the same.
One human kidney width is about 5-6 cm, 11.5-12.5 cm in length and 3-4 cm in thickness. Usually the left kidney is slightly larger than the right kidney.
The structure of the kidney
How do the kidneys look if we look at this organ in more detail? Each kidney is covered with a fibrous connective tissue capsule, and inside consists of a system of accumulation and excretion of urine and parenchyma.
- The capsule of the kidney is a dense cover of connective tissue.
- The parenchyma consists of a layer of cortical substance and a layer of medulla.
- The system of accumulation and excretion of urine is a small kidney calyx, which, merging, form one large calyx. Large kidney cups, in turn, form a pelvis.
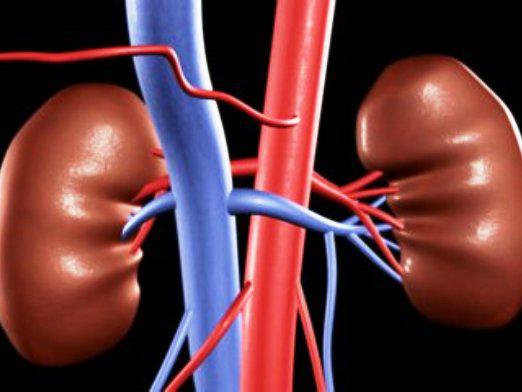
- The renal pelvis passes into the right and left ureters, which lead to the bladder.
The kidneys perform a number of specific functions inorganism. The main of them is the filtration of blood and, accordingly, the excretory function, which is the formation of urine. In the urine get all the harmful impurities of blood filtered by this body.
Two-stage filtration
The filtration of blood takes place in two stages. The first forms the primary urine. To do this, blood elements are allocated from the blood (erythrocytes, platelets and white blood cells) and proteins. This process is called ultrafiltration. In addition to the products of vital activity, the primary urine also contains useful substances, such as mineral salts, as well as organic compounds.
At the second stage of filtration from the primarysecondary urine is formed by removing the remaining nutrients from it, as well as excess fluid that is sent back to the bloodstream. Secondary urine enters the bladder.
Nephrons
The filtration of blood passes in the kidney tissue. If you look at how the kidneys look under the microscope, you can see the nephrons - the functional units of the kidney tissue. The human kidney contains about 1 million nephrons. Functional nephron can be divided into three systems:
- the circulatory;
- a Bowman-Shumlyansky capsule;
- system of tubules.
Ultrafiltration occurs in a capsuleBowman-Shumlyansky. Through a layer that is impervious to shaped elements, the blood (turning into the primary urine, which the body daily forms about 180 liters) enters the tubule system. In them passes both passive (not spending energy of the organism) and active (with energy costs) transport of substances. As a result, the bulk of the fluid and nutrients from the primary urine returns to the body. While uric acid, creatinine, other metabolic products, as well as toxins dissolved in a small volume of water, are sent to the bladder for excretion along with urine.