How do I disassemble a member proposal?

Watch the video


Members of a sentence are structural componentsThe sentence is complete in the semantic plan of the unit of speech. Members of the proposal differ from each other in the functions they perform in the proposal. Each member of the sentence can be expressed in a single word or in a phrase.
What are the members of the proposal
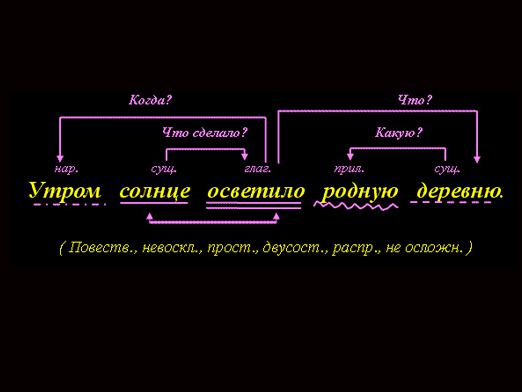
In order to parse by sentence members, we need to recall what the members of a sentence are in principle. All members of the sentence are divided into main and secondary.
The main subject is the subject and the predicate. The subject calls the person mentioned in the statement the carrier of the action. The predicate conveys information about the action or state of the subject. Subjects and predicate form the grammatical basis of the sentence. If there is one basis in the sentence, it is simple, if two are complex.
Secondary members are supplement(names objects to which the action is directed), definition (calls for attributes of objects) and circumstances (report on time, place, mode of action).
Discussion of the proposals for members
Let's take a light version - a simple sentence. His analysis begins with finding the main members of the sentence. The subject will answer the question who? or what? and expressed by a noun in the nominative case or pronoun, can be an infinitive. The predicate answers the question of what to do? and is expressed by the verb. Having found the main terms, we emphasize the subject with one solid line, and the predicate is two. Note that there are sentences that contain only the subject or only the predicate.
The next step in analyzing the proposal is finding its secondary members. The secondary members will depend on the other members of the proposal and supplement the information transmitted by them.
The addition in the sentence is expressed by a noun or pronoun, answers questions of indirect cases and is emphasized by a broken line.
The definition answers the questions of what? what ?, is expressed in the name of the adjective, participle, pronoun and is highlighted by underscores with a wavy line.
Circumstance answers the questions where? as? why? where? why ?, is emphasized by a dashed line with dots. Expressed by an adverb, a gerund, a noun, an infinitive.
A special case is the analysis of the proposal withhomogeneous terms. Homogeneous members of the sentence perform the same function in it and answer the same questions. All members of the sentence can be homogeneous: both main and secondary. This means that there can be two or more subjects in the sentence, two or more predicates, etc. Homogeneous members usually follow one another, separated from each other by commas or joined by a union.
If the sentence is complex, that is, it has two grammatical foundations, similarly it understands not only the main sentence, but also subordinate to it.
Let's consider a simple example. In the sentence "Everyone prepares a sleigh for summer", the word "everyone" (who?) Is the subject, "prepare" (what they do?) - the predicate, "sleigh" (prepare what?) - addition, "in the summer" (cook when?) - circumstance.
Learn also how to parse a sentence by parts of speech.