What is the parenchyma?
When we talk about different types of tissues inthe body of animals and humans, we usually indicate the presence of epithelial, connective, nervous and muscle tissues. However, few know that some organs of living organisms have special accumulations of basic functioning elements, called parenchyma. This is also a kind of fabric that has certain properties and functions. In this article we will describe what parenchyma is and what diseases can be associated with it.
The meaning of the term
The term parenchyma may have two interpretations. If we are talking about the parenchyma of plants, then we are talking about homogeneous clusters of soft tissues in the body of the plant that fill the space between other tissues and serve to accumulate water and nutrients, and to support the plant stem.
If we talk about the parenchyma of animals, herewe are talking about tissue, which is the main part of most organs and is responsible for their normal functioning. Especially often in medical articles mention parenchyma of the kidneys, liver, thyroid and other organs.
Diseases
The most common problems associated with the parenchyma arise in the kidney and liver. In this regard, we should mention such pathologies of the parenchyma as:
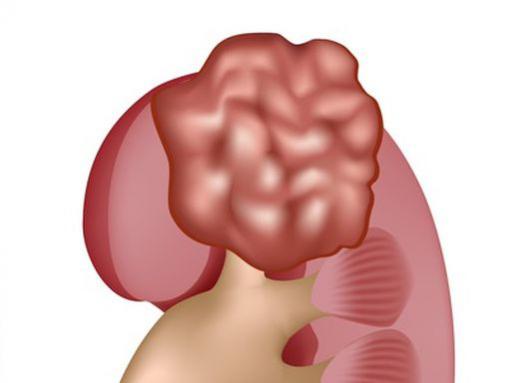
- Tumor of the parenchyma is the appearance of malignant (cancer) or benign (oncocytoma, adenoma, angiomyolipoma) formations in internal organs, usually in the kidneys.
- Diffuse changes in the parenchyma is a changetissue density, which can be associated with such diseases as acute hepatitis, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, fatty infiltration, urolithiasis, kidney stones, pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus, etc.
- The cyst of the parenchyma is the appearance of a benign, thin-walled neoplasm, usually from a serous fluid.
- Thinening of the parenchyma leads to a decrease in the size of the organ under the influence of the transferred infections and improperly selected medications.
- Calcium parenchyma is the accumulation of calcium salts invarious organs that occurred as a result of the transferred disease (for example, as a result of tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, etc.).
- Reactive changes in the parenchyma - the change in tissue under the influence of the inflammatory process, which can be accompanied by pain syndrome, dyspepsia and increased blood sugar.
As can be seen from the examples, the changeParenchyma does not cause the appearance of diseases, but is their consequence. To avoid such changes, it is first necessary to establish and eliminate the cause of their occurrence. For the diagnosis of parenchyma of various organs, the most effective methods are ultrasound, computed tomography, x-ray, screening, etc.
Read also the article What is diffuse liver changes.